In its Annual Report for 2024-25, NABARD highlighted that India’s cooperative banking sector registered steady growth in FY2024, with both State Cooperative Banks (StCBs) and District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) recording strong performance across financial parameters.
The short-term cooperative credit structure (STCCS) comprises 34 StCBs with 2,140 branches, 351 DCCBs with 13,759 branches, and nearly 1.06 lakh Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS). Collectively, these institutions serve close to 6.5 lakh villages, acting as the backbone of rural credit delivery.
On the financial front, StCBs’ share capital grew 7.7% to Rs 10,531 crore, while DCCBs recorded an 8.2% rise to Rs 28,661 crore. Reserves also expanded, reaching Rs 22,861 crore for StCBs and Rs 31,701 crore for DCCBs. Deposits saw steady growth, with StCBs mobilizing Rs 2,56,819 crore (up 6%) and DCCBs achieving a stronger 10% increase to Rs 4,76,610 crore.
Borrowings and investments trended upwards as well. StCBs’ borrowings surged 11.7% to Rs 1,73,100 crore, compared to a 9.9% increase in DCCBs to Rs 1,61,700 crore. Investments rose to Rs 1,55,800 crore for StCBs and Rs 2,65,700 crore for DCCBs.
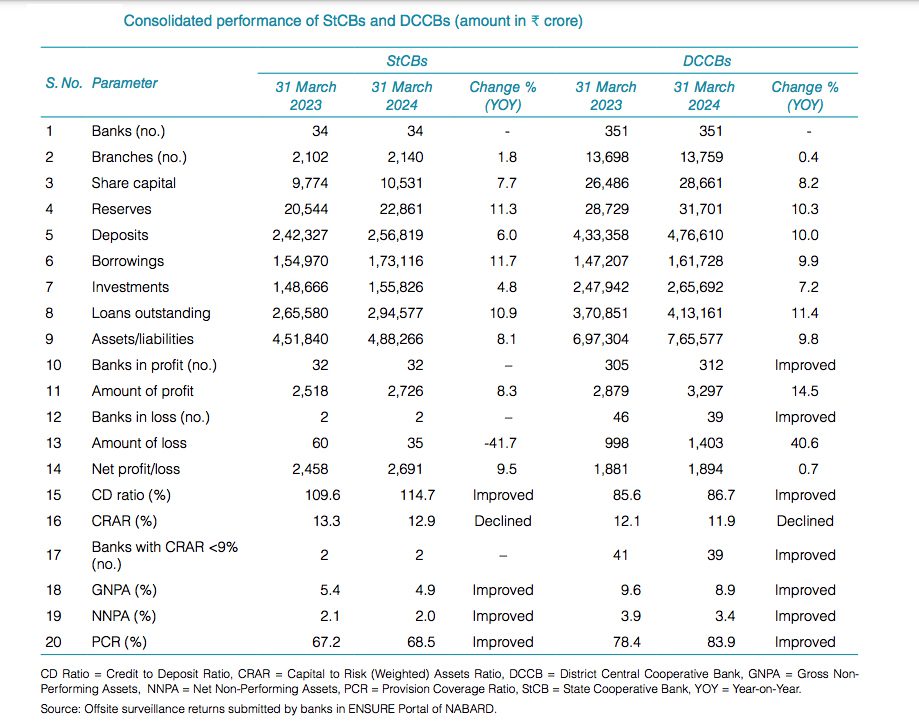

Profitability indicators reflected encouraging trends. Of the 34 StCBs, 32 reported profits amounting to Rs 2,691 crore, up 9.5% from the previous year. DCCBs also improved, with profit-making banks increasing from 305 to 312, and net profits rising 14.5% to Rs 3,297 crore. However, losses at DCCBs inched up to Rs 1,403 crore, though fewer banks reported negative results.
Key ratios showed a mixed picture. The credit-to-deposit (CD) ratio improved to 114.7% for StCBs and 86.7% for DCCBs, signaling stronger credit deployment. Capital adequacy (CRAR) slipped marginally to 12.9% and 11.9% respectively.
Asset quality strengthened, with gross NPAs declining to 4.9% for StCBs and 8.9% for DCCBs, while net NPAs eased to 2.0% and 3.4%. Provision coverage ratios (PCR) improved sharply, standing at 68.5% for StCBs and 83.9% for DCCBs.
Structurally, India’s cooperative credit system remains diverse. Twelve states follow a three-tier system (StCBs–DCCBs–PACS), fifteen states operate under a two-tier framework, and seven have adopted a mixed model.
Beyond the short-term structure, the long-term cooperative credit system (LTCCS) consists of 13 State Cooperative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (SCARDBs) with 692 branches and 608 Primary Cooperative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (PCARDBs). Additionally, 43 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) operate through 22,158 branches across 26 states and 3 Union Territories.
While DCCBs continue to dominate in terms of size, mobilizing deposits of nearly Rs 4.8 lakh crore and loans exceeding Rs 4.1 lakh crore, StCBs posted sharper growth in borrowings and credit. This underlines their growing importance in India’s financial ecosystem, even as DCCBs remain the larger players in the cooperative credit landscape.