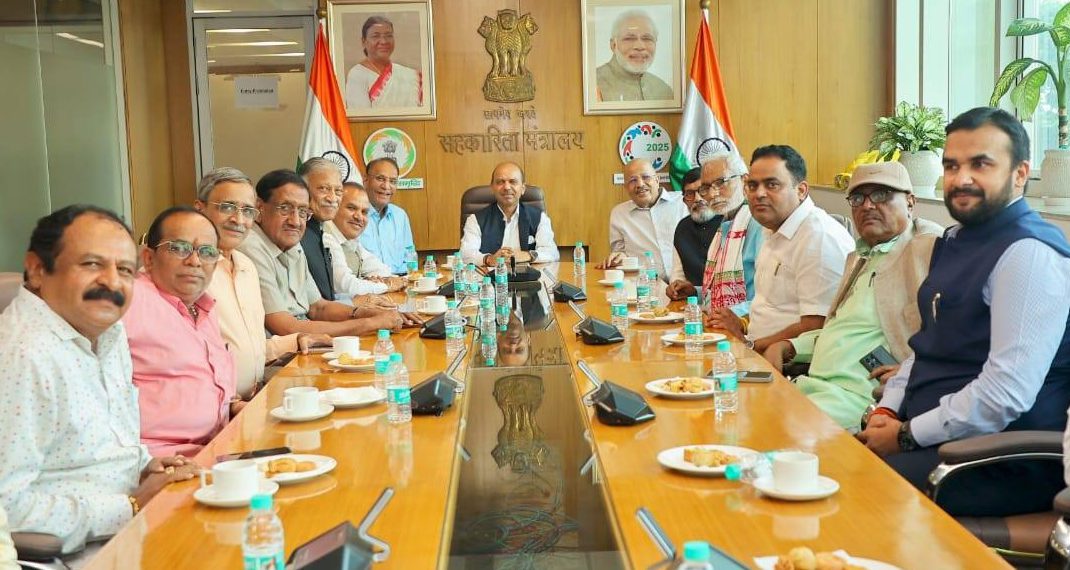
The Cooperative Bank of India (COBI), recently notified under the Second Schedule of the Multi-State Co-operative Societies (MSCS) Act, 2002, convened a high-level meeting with the Union Ministry of Cooperation to chalk out its roadmap for obtaining a banking license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and completing its transition into a national-level cooperative banking institution.
The meeting, chaired by Cooperation Secretary Dr. Ashish Kumar Bhutani at the Atal Akshay Urja Bhawan, focused on licensing requirements, strengthening governance, and aligning COBI’s operations with its new legal framework. Senior officials including Joint Secretary Raman Kumar and Director Kumar Rama Krishna attended.
On COBI’s behalf, Chairman Ajay Patel led a delegation comprising Vice Chairman G.H. Amin, ICA-AP President Dr. Chandrapal Singh Yadav, NAFED Chairman Jethabhai Ahir, Nafscob Chairman Ravinder Rao, NCCF Chairman Vishal Singh, CA Milind Kale, Rudragouda Patil, and Managing Director V.K. Dubey, among others. A detailed presentation on COBI’s activities and progress was also shared.
Secretary Bhutani praised the role of cooperatives in financial inclusion and emphasized the need for digitization, innovation, and modernization to serve rural and semi-urban India. He assured full Ministry support in expediting the RBI approval process.
The deliberations also flagged challenges such as liquidity flow, compliance requirements, and building digital infrastructure, with leaders underscoring the importance of government–cooperative collaboration in shaping COBI into a robust institution.
The meeting concluded with a vote of thanks from Vice Chairman G.H. Amin. Later, COBI’s Board met at the NCUI Building to continue discussions on its roadmap.
Observers highlighted that the presence of top cooperative leaders reflected the high expectations surrounding COBI’s emergence as India’s national-level cooperative bank.
Notably, the long-pending formulation of COBI, stalled for nearly two decades, gained momentum only after the intervention of Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah, whose efforts ensured COBI’s inclusion in the Second Schedule of the MSCS Act, 2002.
The Cooperative Bank of India (COBI), established in 1993 on the recommendation of the RBI’s High-Level Agriculture Credit Review Committee, was created to strengthen the cooperative credit system and promote “Sahkar Se Samridhi.”
COBI facilitates fund transfers between cooperatives and other banks, provides finance for rural infrastructure, agro-industries, fisheries, dairies, and technology upgradation, and extends liquidity support to cooperative banks. It also supports international trade, manages institutional protection funds, raises resources from global agencies, deals in securities, and acts as a Payment Service Provider.
Additionally, COBI undertakes research, consultancy, training, and technology services to strengthen the cooperative sector.