In its “Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2023-24” report, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) presented a mixed outlook for Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs). While UCBs saw improvements in capital buffers, profitability, and asset quality, their growth in credit and deposits remained subdued compared to commercial banks, reflecting ongoing challenges in the sector.
According to the RBI, UCBs have made strides in enhancing governance and risk management, with significant initiatives aimed at strengthening operational frameworks.
These include the introduction of a four-tiered regulatory structure, direct engagement with UCB board directors and heads of assurance functions, and a focus on IT and cybersecurity risks.
Despite these advancements, UCBs’ credit and deposit growth remained relatively stagnant, with credit growth at just 5 percent and deposits up by a marginal 4.1 percent during 2023-24.
The report also shed light on the long-term consolidation efforts in the UCB sector, which began in 2004-05 to address the financial instability of many UCBs that had surged in the 1990s due to a liberal licensing policy.
Since then, 156 UCB mergers have taken place, with six in 2023-24 alone. The majority of these mergers occurred in Maharashtra, followed by Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh. However, the cancellation of UCB licenses also continued, with 24 cancellations during 2023-24, bringing the total to 70 since 2015-16, primarily in the non-scheduled category.
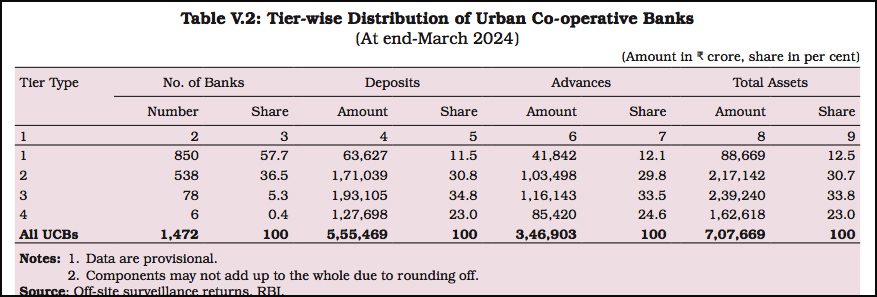

In terms of asset distribution, UCBs have seen a shift towards larger institutions, with 44.3 percent of UCBs falling in the Rs 50 crore to Rs 250 crore asset class in 2023-24. The share of SLR investments in UCBs remains high, though their investment growth is still lagging behind that of SCBs.
Profitability, although impacted by increased expenditure, improved in terms of net profits due to lower provisions for bad loans. The gross non-performing asset (GNPA) ratio for UCBs declined to 9.6 percent in September 2024, down from 10.9 percent a year earlier. The provision coverage ratio (PCR) also showed improvement, aided by a decline in NPA levels.
UCBs’ role in the cooperative banking sector remains significant, with 1,472 UCBs and over 1 lakh rural credit cooperatives (RCCs) operating across India. However, the dominance of primary agricultural credit societies (PACS) continues, making up over 97 percent of the cooperative banking institutions, though their share in assets is much smaller, at 17.8 percent of the total cooperative sector.
As UCBs continue to navigate challenges in a changing financial landscape, the RBI’s report underscores ongoing efforts to strengthen the sector’s governance, risk management, and operational efficiency. However, the road to recovery and growth remains long, with consolidation and strategic reforms likely to shape the future trajectory of UCBs in India.